Furniture manufacturing industry
The furniture manufacturing industry is one of the sectors with significant emissions of spray painting exhaust gases. During furniture manufacturing, painting processes generate a large amount of organic exhaust gases. However, painting is one of the most critical processes in furniture manufacturing, directly affecting the appearance, quality, and value of the furniture.In the past, many companies temporarily addressed VOC emissions using water washing or dust removal methods, but the results were often unsatisfactory. In recent years, many leading companies in the industry have begun to adopt a combination of adsorption and catalytic processes, achieving excellent purification results.
Features
A single production line typically has an air volume of about 10,000 m³/h to 30,000 m³/h.
Often, several spray booths share one exhaust gas treatment system.
The exhaust gas concentration ranges from 200 mg/m³ to 1000 mg/m³, often accompanied by significant dust.
Main components: benzene series compounds, alcohols, and esters. With the widespread adoption of UV paint curing technology, the exhaust gas also contains a high amount of acrylate monomers.
Common Practices
Traditional Processes
Traditional exhaust gas treatment equipment in the furniture industry is generally quite conventional, including simple activated carbon adsorption, photolysis, plasma, and water washing. These types of equipment typically can only address particulate matter and small amounts of VOCs and cannot continuously and efficiently treat VOCs. Plasma equipment, in particular, has a significant fire hazard and has been banned in many places. In recent years, environmental policies introduced in various regions strictly prohibit the use of single activated carbon and photolysis equipment. As a result, combined processes have become the mainstream for treating spray painting exhaust gases.
- Adsorption-Desorption + Catalytic Combustion
The conventional solution is to remove dust from the exhaust gas through water washing, followed by using activated carbon adsorption-desorption + catalytic combustion to treat high volume,low-concentration exhaust gas. In recent years, due to incidents of spontaneous combustion in activated carbon adsorption-desorption processes and the inability to continuously meet standards, some companies have started using zeolite wheel or zeolite fixed bed adsorption + catalytic combustion processes. The use of zeolite adsorption technology has made it possible for exhaust gases from furniture manufacturing to consistently meet standards and comply with online monitoring requirements.
As environmental requirements become increasingly stringent, many furniture manufacturing companies are seeking better solutions. Among these, zeolite fixed bed and zeolite wheel adsorption technologies have become focal points of interest. FT Technology recommends that if the exhaust gas emissions are continuous and stable with concentrations higher than 500 mg/m³, using a zeolite wheel + catalytic combustion process is appropriate. For non-continuous emissions or lower concentrations, a zeolite fixed bed + catalytic combustion process is more suitable.
Recommended Products
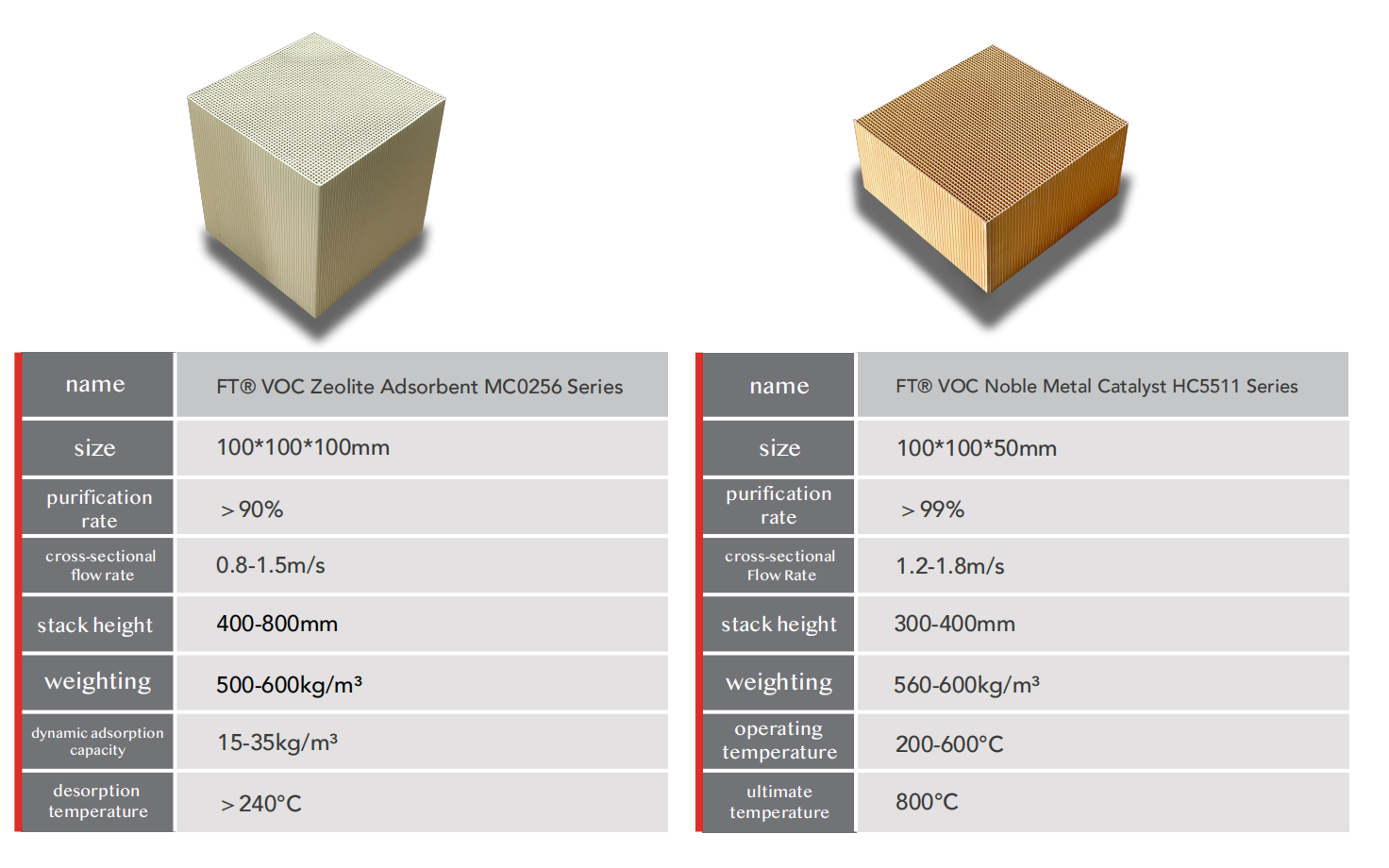
New Trends
As the level of intelligence and standardization in furniture manufacturing increases, production pace and emission requirements also rise. Water-based coatings and UV coatings have become market favorites due to their low emissions and high efficiency. In response to these market changes, zeolite fixed beds, with their high concentration ratio and excellent purification rate, have emerged as one of the new solutions.
In the production process of water-based coatings, VOC emissions are very low (generally below 50 mg/m³). Zeolite honeycombs are more suitable for treating such ultra-low concentration exhaust gases. Additionally, in UV coatings, photoinitiators can quickly generate free radical ions under UV light, triggering the polymerization and cross-linking of resins and active monomers.After long-term adsorption and desorption, periodic high-temperature regeneration is required. Currently, the zeolite fixed bed adsorption-desorption process has become the main method for handling these two types of exhaust gases.

