Packaging and Printing Industry
The exhaust gases from the packaging and printing industry mainly include benzene series compounds, esters, alcohols, and ketones. With the promotion of wind reduction and concentration enhancement technology in recent years, the concentration of exhaust gases has gradually increased. The use of zeolite wheel + catalytic combustion technology or direct RTO (Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer) treatment has become common. However, during the treatment process, fluctuations in the inlet gas concentration often lead to unstable emissions. Additionally, some RTO equipment may not achieve a conversion rate of over 98%, resulting in the risk of exceeding the exhaust concentration limits.
Features
- High air volume, approximately between 20,000 m³/h and 100,000 m³/h.
- Wide concentration range, approximately between 300 mg/m³ and 3000 mg/m³.
- Inlet concentration fluctuates significantly with varying production line utilization rates. When production products change, exhaust gas composition also changes
- Main components: benzene series compounds, ketones, alcohols, esters, etc.
Common Practices
- Direct RTO/RCO
When the inlet concentration is high, RTO equipment is used for direct high-temperature incineration, leveraging the high removal efficiency of RTO to eliminate a large amount of VOCs. However,a potential issue with this process is the risk of exceeding emission standards if the inlet concentration is too high. If the concentration is not particularly high, RCO equipment can be used for treatment, ensuring compliant emissions while reducing reaction temperature and system energy consumption.
- Zeolite adsorption-desorption + catalytic combustion/RTO
This process uses zeolite as the adsorption and desorption material, primarily in the forms of zeolite wheels, zeolite drums, and honeycomb zeolite for continuous adsorption and desorption.The entire equipment setup can generally maintain a purification efficiency of around 90% for several years.
Due to the diverse categories within the packaging and printing industry, the types and concentrations of exhaust gases are complex and variable. Generally, equipment needs to have good capacity. For projects with higher and stable concentrations, RTO/RCO can be used. For projects with concentrations lower than 1000 mg/m³, a combination of adsorption-desorption and destruction technologies is required for treatment.Given the market conditions, FT Technology recommends using the high-temperature-resistant catalyst HC6541 in combination with the "Zeolite Wheel (or Fixed Bed) Adsorption Concentration + Catalytic Combustion Technology." This technology involves adsorbing exhaust gases using zeolite adsorbents, then desorbing and combusting the concentrated exhaust gases using catalytic combustion. The generated thermal energy continuously circulates internally for desorption. The outstanding high-temperature resistance of this product ensures high catalytic efficiency in the wheel desorption system.
For packaging and printing exhaust gases, RCO devices can use either HC5641 or HC6541. With a catalytic efficiency exceeding 99%, these products ensure that RCOequipment can achieve the same high purification rate as RTO while saving energy for the owner.
Recommended Products
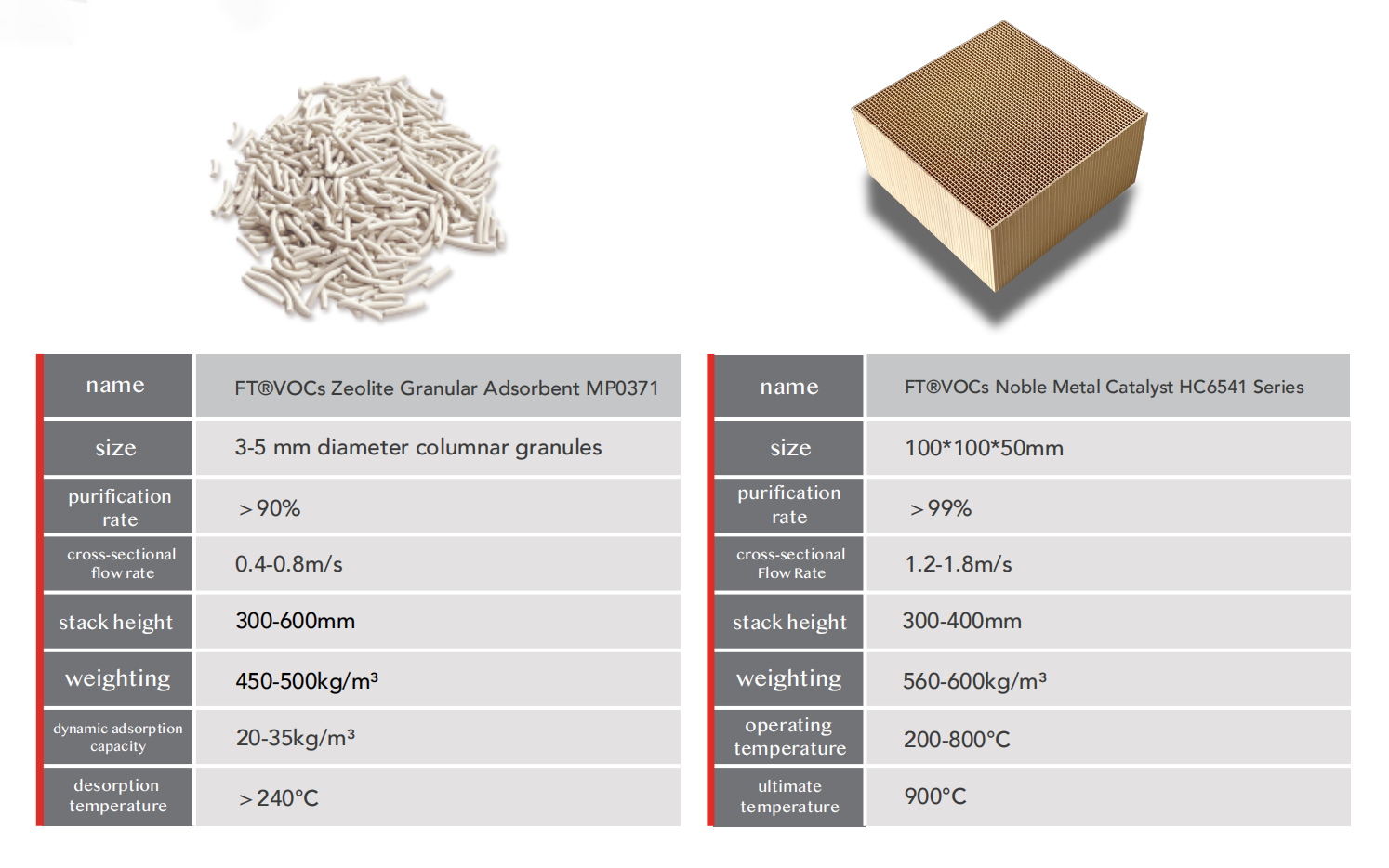
New Trends
For low concentrations: Activated carbon adsorption-desorption + catalytic combustion.
For conventional concentrations: Zeolite wheel (fixed bed) adsorption-desorption + catalytic combustion.
For high concentrations: RTO/RCO.
In the printing and packaging industry, catalytic combustion technology is often used in the equipment to recycle energy due to the use of thermal ovens for drying coatings. However, the issue of end emissions remains severe. Currently, using zeolite fixed bed or zeolite wheel + catalytic combustion technology has become a viable process. Ordinary activated carbon adsorption technology struggles to achieve truly effective compliance with standards.

